
What Causes Joint Pain?
Pain in the joints is not just uncomfortable, but also can be unbearably painful, and can even alter your way of living. The pain and other conditions, such as hardening or stiffening of the joints, can cause difficulty with even simple movements. The joint’s condition not only affects the patient physically, but can also cause some psychological stress as well. Contrary to popular belief, joint pain is not only caused by joint degeneration. Other physical conditions or maladies may also trigger symptoms.
 The most common joint disorders damage the joints and even the surrounding areas. They can develop from aging, malnutrition, untreated physical trauma or even genetics. Although common they are often irreversible with symptoms ranging from mild to moderate to severe. In worst cases they can even contribute to the death of the patient due to complications involving major organs.
The most common joint disorders damage the joints and even the surrounding areas. They can develop from aging, malnutrition, untreated physical trauma or even genetics. Although common they are often irreversible with symptoms ranging from mild to moderate to severe. In worst cases they can even contribute to the death of the patient due to complications involving major organs.
Other Causes of Joint Pain
On the other hand, an infection followed by swelling or inflammation, can also cause joint pain. Having joint pain does not automatically mean that the person is suffering from a joint disorder. Consider that humans have upwards of 250 joints and it is only normal to experience some joint pain, especially after physically stressful activity. In fact, a simple pain reliever or anti-inflammatory drugs available over the counter in any pharmacy can resolve most of these joint complaints.
 Physical trauma such as “wear and tear” to the joints can also cause joint-problem symptoms. Pressure on the joints can cause damage, which normally swells or gets inflamed. Athletes or those involved in physical work such as construction can routinely experience this type of joint trauma.
Physical trauma such as “wear and tear” to the joints can also cause joint-problem symptoms. Pressure on the joints can cause damage, which normally swells or gets inflamed. Athletes or those involved in physical work such as construction can routinely experience this type of joint trauma.
The inflammation or swelling of the joints causes pain, too. Any joints that continuously receive pressure from excessive weight or from constant movement and activities, can cause “wear and tear” or injury to the joints that can lead to infection.
Treating the inflammation usually reduces the pain as well since that is the usual reason for the pain. Many types of anti-inflammatory medications in the market or pharmacy are available over the counter.
Joint pain can also appear when people use their muscles or joints all the time, without rest. For example, gym goers usually experience these symptoms after undergoing serious workout or exercises. This is due to the pressure applied to the muscles and the joints. Warm bath or steaming can relax the muscles and reduce the pain in the joint area. In some cases, a cold compress resolves the joint pain problem, especially when caused by an injury.
As mentioned above, pain in the joints can be very uncomfortable and it can immobilize a person from doing even the simplest daily activities; this usually causes mental or psychological stress to the patient, and even can cause the pain to worsen.
Dealing and Finding Solutions
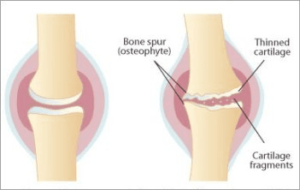 Since there is no cure for the most common joint conditions, the next best solution is to deal with the symptoms. With a degenerative joint condition, patients often joint pain during the first part of the day but it subsides with movement during the day. Simple exercises can help alleviate joint pain and prevent joint hardening. This improves both the range and motion of the joints when a joint disorder is already present.
Since there is no cure for the most common joint conditions, the next best solution is to deal with the symptoms. With a degenerative joint condition, patients often joint pain during the first part of the day but it subsides with movement during the day. Simple exercises can help alleviate joint pain and prevent joint hardening. This improves both the range and motion of the joints when a joint disorder is already present.
There are times when pain in the joints comes from lack of movement. That is why it is important for patients with joint pain, even for those without a diagnosis of one of the common joint conditions, to engage their joints in some gentle stretching, achieved by walking or jogging. Even the simplest exercises help improve elasticity and increase the lubrication of the joints and the muscles that support that area, as well as promote the healing process if there is damage in the joints.
For those who feel frequent joint pain, this may be a sign that a doctor’s intervention is already necessary. Recurrent joint pain can be a sign of a condition triggering it. Early detection is important in order to effectively delay the progression of many joint conditions, enabling doctors to offer a better range of treatments and medications to minimize the symptoms.
TOP 5
JOINTTreatments |
|||||
| Jointlax | Joint Advance | Exomine | Carlson Nutra-Support Joint | Himalya JointCare | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Price (1 bottle) Price (6 bottles)best value |
$49.95 $139.0 |
$39.95 $239.70 |
$59.95 $239.70 |
$56.50 $339.00 |
$29.95 $179.70 |
| Overall Rating | 99.50% | 91% | 78.30% | 72.00% | 69% |
| Performance* |





|





|





|





|





|
| Speed of Results* | Extremely Fast | Good | Average | Average | Slow |
| Quality of Ingredients | Premium | Good | Good | Average | Unknown |
| Customer Satisfaction Evaluation | 99.20% | 87% | 76.20% | 72% | 66.30% |
| Safety Evaluation | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use |
| Customer Service Rating |





|





|





|





|





|
| Reorder Rate | Highest | Good | Good | Average | Average |
| Return Policy | Risk Free | Unopened | Unopened | Risk Free | No |
| Success Rate | 99.40% | 82.50% | 74% | 71.20% | 62% |

 Subscribe Now
Subscribe Now











